Joint effusion is one of the most common and debilitating conditions affecting patient mobility. Moreover, if joint effusion persists, it can lead to joint infections due to repeated fluid accumulation. It can even damage the joint, affecting its mobility function.
NỘI DUNG CHÍNH
1. What is joint effusion?
In the structure of the knee joint, there is always a type of fluid called synovial fluid. The role of this fluid is to lubricate the cartilage, reduce friction when the two ends of the bones rub against each other, and nourish the joint cartilage. At the same time, it ensures the joint remains smooth during movement.
Joint effusion is when synovial fluid is excessively secreted inside and around the joint, causing the knee to become swollen, edematous, and painful when in motion.
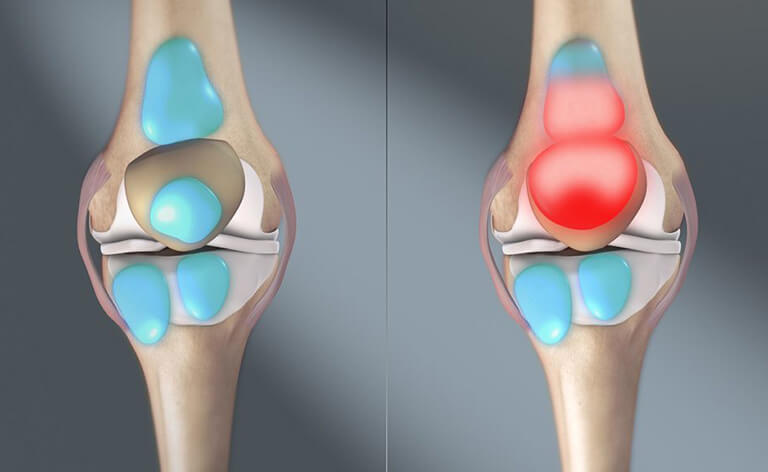
2. Signs of joint effusion
Any joint can experience this condition, but the knee joint is the most commonly affected. In the early stages of joint effusion, the symptoms are relatively easy to recognize:
- Swelling: The knee becomes enlarged, swollen, and feels tight due to the accumulation of excess synovial fluid, causing discomfort.
- Pain and discomfort: Patients may experience a heavier feeling in the knee or persistent dull, throbbing pain, especially when putting pressure on the knee.
- Stiffness: Particularly noticeable when bending or straightening the knee, climbing stairs, or transitioning between sitting and standing.
- Warmth and redness around the knee, which feels tender.
- The affected knee appears more extensive than the unaffected one.
- If joint effusion occurs after an injury, it may be accompanied by bruising or bleeding within the joint.
3. Causes of joint effusion?
Joint effusion can be caused by various factors, including:
- Trauma: Injuries during work, sports, or daily activities can damage ligaments, tear joint cartilage, and harm knee joint structures, leading to increased synovial fluid production and joint swelling.
- Joint infection: Patients infected with viruses or bacteria, such as psoriasis, tuberculosis, or post-traumatic diseases that are not adequately treated, can develop joint effusion.
- Weight gain: Excessive body weight puts additional pressure on the knee joint, potentially leading to synovial fluid overproduction and joint swelling. Prolonged weight-related joint stress can lead to further damage.
- Joint disorders: Conditions like osteoarthritis, gout, and rheumatoid arthritis contribute to joint effusion.
To accurately determine the cause of joint effusion, patients should seek specialized medical care for thorough examination and diagnostic imaging. Self-diagnosis and home treatment are discouraged as they may exacerbate the condition.

4. Is joint effusion dangerous?
In reality, very few cases of joint effusion resolve spontaneously. Early intervention can lead to complete recovery without complications. However, if treatment is delayed, serious consequences may occur, including:
- Persistent and debilitating pain leading to weakness and fatigue.
- Joint stiffness, adhesion, and even joint infections.
- Joint damage and deformity.
- Muscle atrophy, paralysis, and loss of mobility.
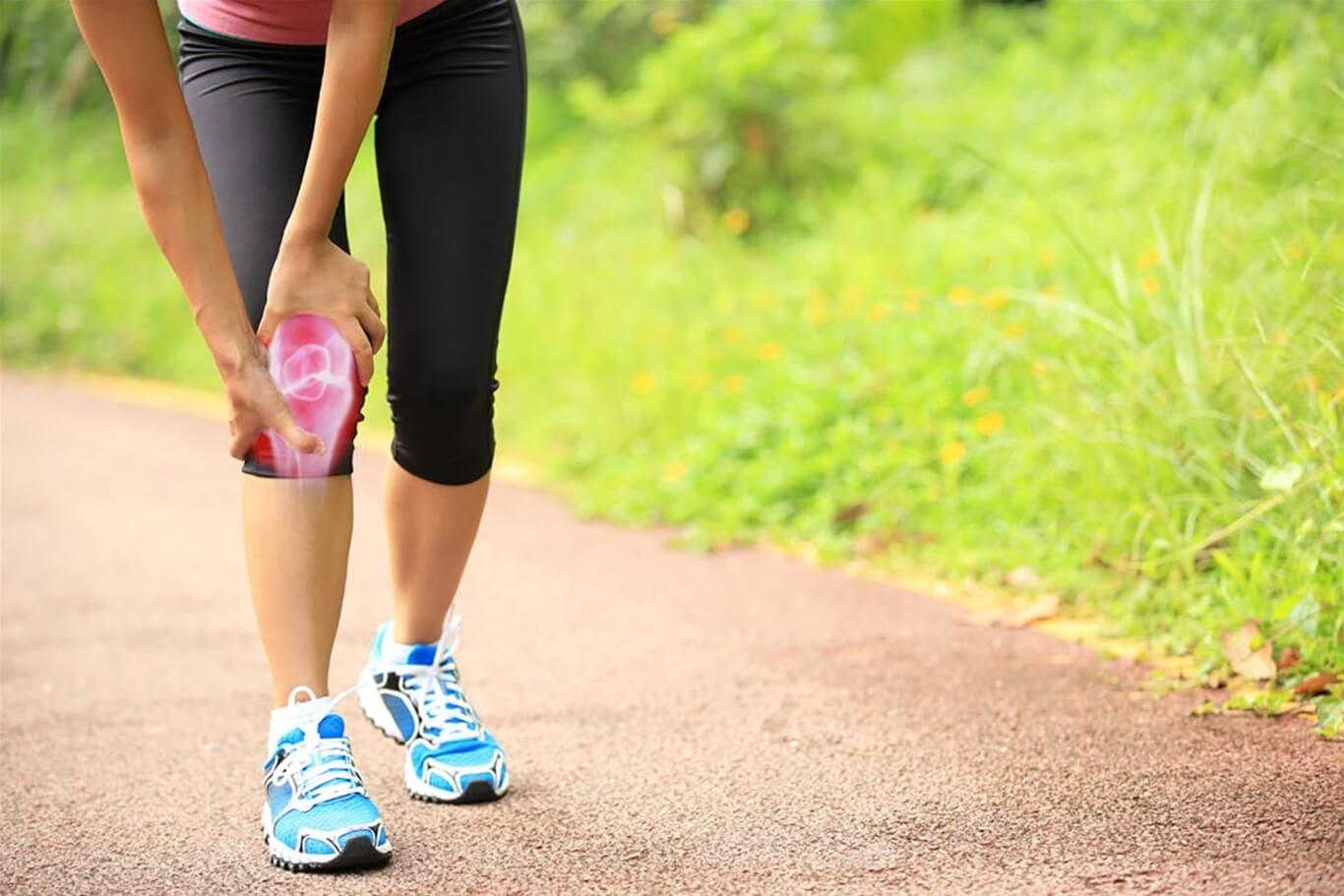

Therefore, patients should seek early treatment to prevent worsening conditions, making subsequent treatment more challenging.
5. Effective treatments for joint effusion ?
Early treatment of joint effusion can lead to complete recovery without complications. However, many individuals neglect their symptoms, allowing the condition to worsen. When they eventually seek medical attention, it can be challenging to manage.
Typically, patients may use pain relievers, antibiotics, or joint fluid aspiration to alleviate pain and treat the condition. However, these methods often provide only temporary relief and do not address the root cause of the disease. Additionally, they can carry potential side effects on internal organs and increase the risk of joint infections.

Stem cell therapy for effective treatment of bone and joint conditions
Bio Nano Cell therapy is the most favored treatment for bone and joint conditions worldwide. Although relatively new in Vietnam, it has shown promising results in treating joint effusion and other degenerative diseases.
Bio Nano Cell therapy operates on the natural healing mechanism of the body, automatically seeking, repairing, and replacing damaged cells due to aging with healthy new cells, resulting in:
- Immediate reduction of swelling, inflammation, and pain.
- Restoration of synovial fluid in the knee joint.
- Regeneration of damaged joint cartilage.
- Improvement in mobility and effective movement.
Importantly, this is the only treatment for joint effusion that is NON-INVASIVE, MEDICATION-FREE, and 100% BIOCOMPATIBLE. Therefore, it is exceptionally safe for elderly patients and those with underlying medical conditions such as heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, and more.



Bài viết liên quan
Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment of Shoulder Osteoarthritis
Shoulder osteoarthritis is a typical joint and bone condition nowadays. It causes pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the shoulder and arm area. Early detection and timely treatment can slow down the progression of the disease. Let AMIO StemCell guide...
Oct
Inflammation Around the Shoulder Joint – A Dangerous Yet Lesser-Known Condition
Inflammation around the shoulder joint with stiffness, also known as adhesive capsulitis or frozen shoulder, is a condition where the shoulder joint becomes stiff due to the formation of scar tissue around it. It thickens and tightens the joint capsule,...
Oct
Achilles Tendonitis – A Common Condition Among Athletes
Achilles tendonitis is a prevalent condition often encountered by athletes or professional sports enthusiasts. Patients typically experience prolonged and challenging discomfort that hampers their daily activities. If not promptly treated, it can lead to various dangerous complications. NỘI DUNG CHÍNH1....
Oct